Tools
Understand how tools extend agent capabilities and enable intelligent workflow automation
What are Tools?
Tools are executable capabilities that extend what agents can do beyond conversation. Unlike simple functions, tools are blueprint-powered, reusable, and intelligent - capable of complex workflows and decision-making.
Create tools with parameters and blueprints, or deploy from templates
Think of tools as specialized AI workers that agents can delegate specific tasks to, like having experts on your team for different functions.
Universal Tool Architecture
Every tool in the Starships.ai framework shares the same core architecture:
Core Components
- Function Interface: JSON schema defining what parameters the tool accepts and returns
- Blueprint Logic: Visual workflow defining exactly how the tool operates
- Configuration: User-specific settings like API keys and custom parameters
- Execution Engine: Secure, isolated runtime environment with timeouts and resource limits
- Explore Integration: Template system for sharing and reusing tools across the community
Blueprint-Powered Architecture
Three Types of Tool Blueprints
Tools in Starships.ai use visual workflows (blueprints) that fall into three main patterns based on complexity and use case:
1. Linear Blueprint (Simple Sequential Flow)
For straightforward operations like calculations, data formatting, or simple API calls:
Use Cases: Calculator tool, time utilities, text processing, unit conversions
2. Branched Blueprint (Conditional Logic)
For tools that need different processing paths based on input or context:
Use Cases: Wikipedia search tool, multi-format processors, API routing tools, content type handlers
3. Loop Blueprint (Retry and State Management)
For tools that need retry logic, error recovery, or iterative processing:
Use Cases: Rate-limited APIs, unreliable external services, batch processing tools, file upload handlers
Blueprint Node Types
All blueprint types can use any combination of these powerful node types:
- start : Receives tool parameters and initiates execution
- code : Executes JavaScript for data processing and validation logic
- conditional : Routes execution based on conditions and business logic
- http_request : Makes raw HTTP calls to external services (absolute URLs)
- connector_action : Makes connector-backed HTTP calls (auth/base URL/mapping from connector templates)
- mutate : Updates tool state and context for complex workflows
- transform : Modifies data structure and format using JSON operations
- end : Returns structured results to the calling agent
Blueprint Architecture: Learn more about the visual workflow system that powers intelligent tool execution.
How Tools Work with Agents
Tools seamlessly integrate with agent conversations through LLM function calling:
Agent Analyzes Request
The agent examines your request and identifies which tools might be helpful to provide a complete answer.
Function Calling Decision
The agent decides to call specific tools with appropriate parameters, like "I need to search for current weather data."
Tool Execution
The tool's blueprint executes with the provided parameters, potentially involving multiple steps like API calls, data processing, and formatting.
Result Integration
The tool result is returned to the agent, who incorporates it into their understanding and continues the conversation.
Example Flow:
User: "What's the current exchange rate for EUR to USD?"
Agent thinks: "I need currency data" → Calls currency-converter tool
Tool executes: API call → data processing → formatted response
Tool returns: "1 EUR = 1.0856 USD (as of 2024-01-15 14:30 UTC)"
Agent responds: "The current EUR to USD exchange rate is 1.0856..."Tool Discovery & Categories
Tools are organized into categories based on their primary function:
- Data & Search: Web search, Wikipedia lookup, document search, data processing, API integration
- Development: Code analysis, documentation generation, testing, deployment automation
- Communication: Email integration, chat platforms, SMS, calendar scheduling
- Utilities: Mathematical operations, time/date tools, text processing, system operations
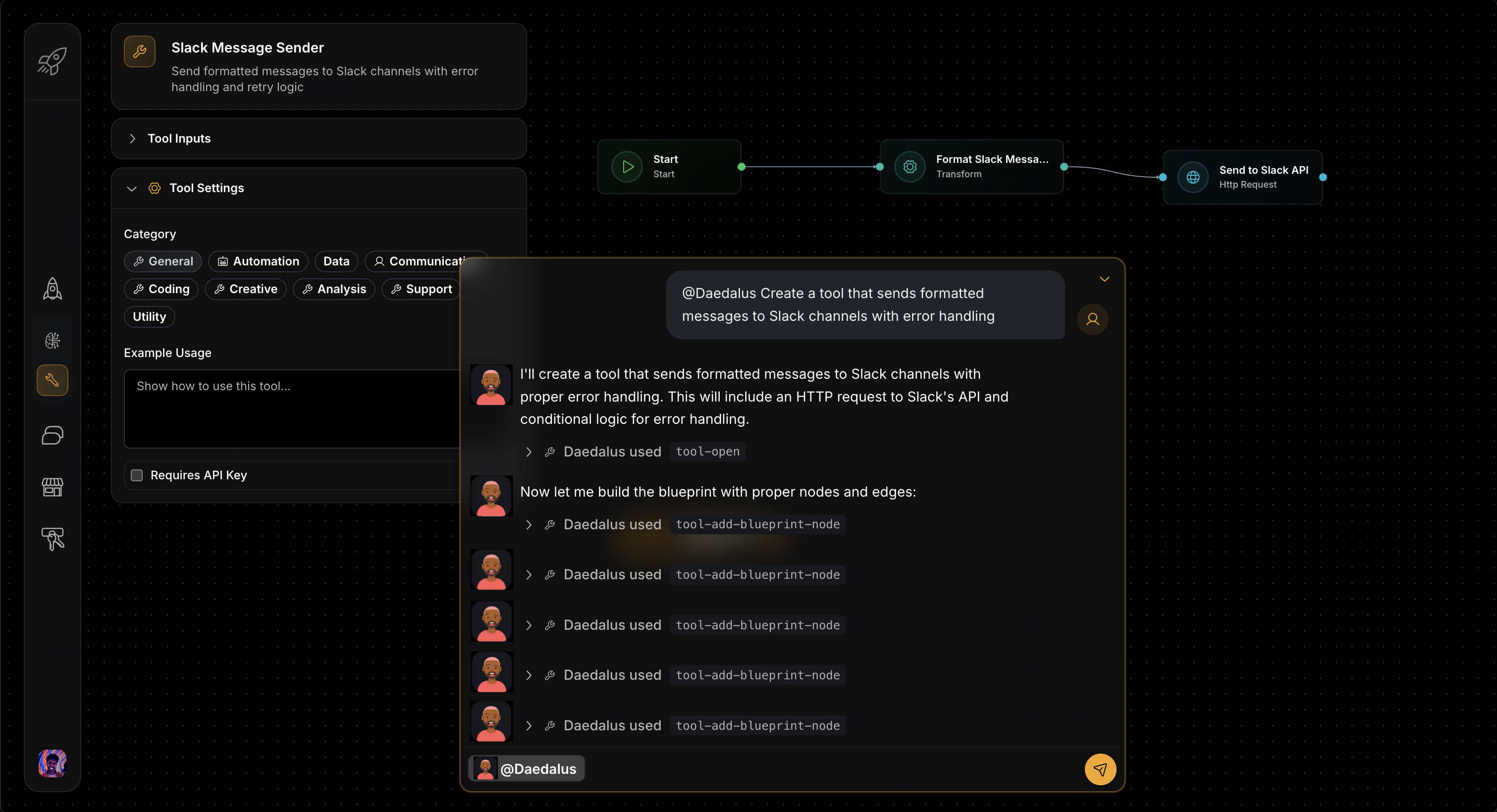
Create Custom Tools with Daedalus
Daedalus is the meta-agent that specializes in creating custom tools through conversation. Build API integrations, data processors, monitoring systems, and automation workflows tailored to your specific needs.
Tool Configuration, Environment Variables & Connectors
When creating custom tools, you can securely store non-secret configuration using environment variables. For many third-party APIs, Starships also provides connectors that guide you through configuration and manage encrypted secrets outside of tool execution.
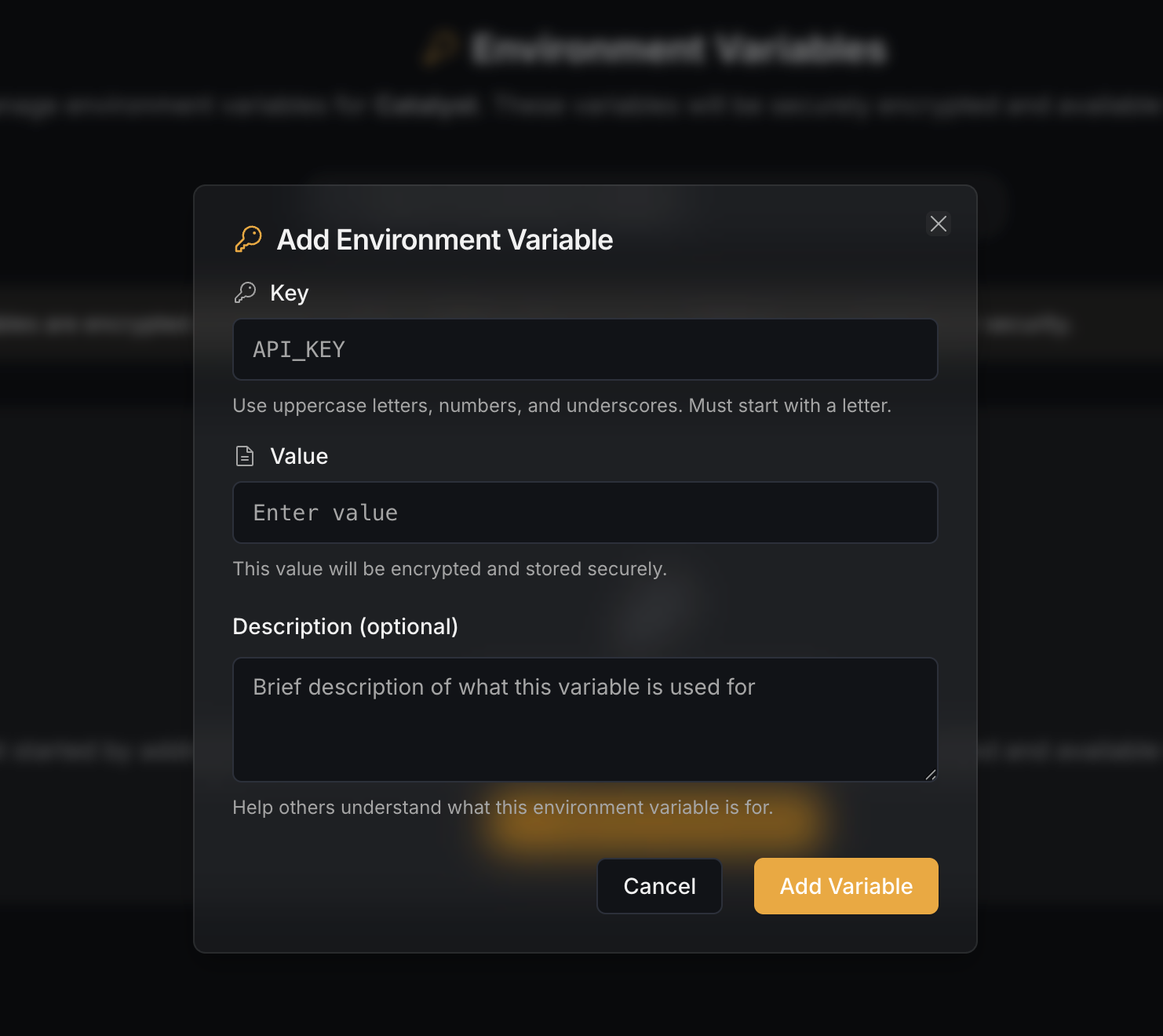
Add environment variables for secure API key storage, or use connectors to populate them automatically
Important (V2 connectors):
- Tool/workflow code does not read connector tokens from env.
- Connector secrets live in:
platform_secrets(instance-wide; instance admins)connector_secrets(per-starship; managed by connect flows)
- Tools call third-party APIs via
connector_action, which injects auth server-side using the connector template + connected starship state. - In the hosted Starships product, agents also rely on
connector_actionfor tool execution authorization/approval (the default Agent loop calls an internal Starships connector endpoint so the server can enforce allow/ask/deny and keep secrets out of blueprints).
Use environment variables for non-secret configuration (defaults, IDs, feature flags). Use connectors for secrets and third-party auth.
Ready to Create Custom Tools? Work with Daedalus to build tools tailored to your specific needs through natural conversation.